categories

Topics

Hair Anatomy

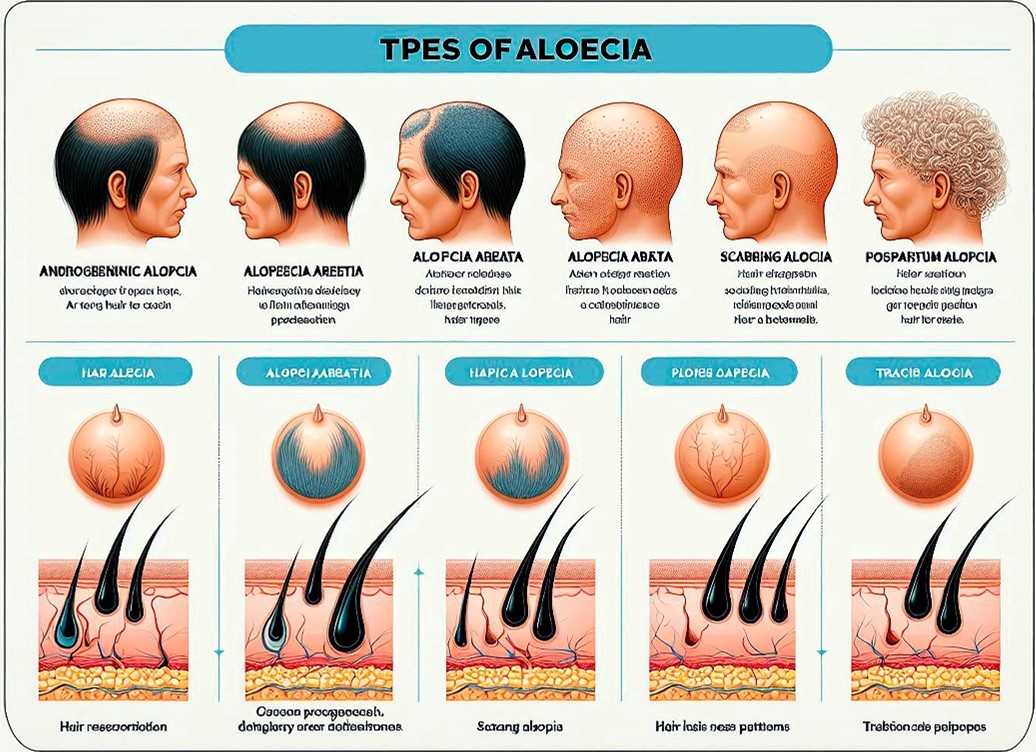
Types of Hair Loss
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Diagnosis
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Treatments
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Surgical Hair Restoration
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Scalp and Hair Health
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hormonal Influence
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Psychological Impact
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Disorders
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
In The News



I’m Dr. Amit Agarkar, a dermatologist and trichologist with over 20 years of experience in helping people regain their hair and confidence. Let’s dive into a topic that affects millions of women—hair loss. It’s a common issue, but it doesn’t have to be your forever reality. Today, I’m going to break down why women experience hair loss, what you can do about it, and the treatments that work best based on my own professional experience