HAIR BASICS

HairBasics
Blogs
Images
Videos
Facebook
X-twitter
Reddit
Pinterest
Whatsapp
Linkedin
Topics

Hair Anatomy

Types of Hair Loss
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Diagnosis
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Treatments
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Surgical Hair Restoration
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Scalp and Hair Health
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hormonal Influence
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Psychological Impact
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Disorders
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Anatomy

Types of Hair Loss
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Diagnosis
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Treatments
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Surgical Hair Restoration
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Scalp and Hair Health
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hormonal Influence
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Psychological Impact
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Disorders
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Anatomy

Types of Hair Loss
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Diagnosis
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Loss Treatments
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Surgical Hair Restoration
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Scalp and Hair Health
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hormonal Influence
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Psychological Impact
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs

Hair Disorders
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- Introduction
- Key Takeaways
- Table of Contents
- Conclusion
- FAQs
In The News
Take A Hair Test
I’m Dr. Amit Agarkar, a dermatologist and trichologist with over 20 years of experience in helping people regain their hair and confidence. Let’s dive into a topic that affects millions of women—hair loss. It’s a common issue, but it doesn’t have to be your forever reality. Today, I’m going to break down why women experience hair loss, what you can do about it, and the treatments that work best based on my own professional experience
Consult Dr.Agarkar
/types-of-hair-loss-dermatologist-guide/
Understanding Types of Hair Loss: Insights from a Dermatologist

Creator & Author: Dr. Amit Agarkar | M.B.B.S, MD Dermatologist, Trichologist & Hair Transplant Surgeon.
- Published On:November 29, 2024
- Time:7:15 pm
- LastUpdated on:November 29, 2024
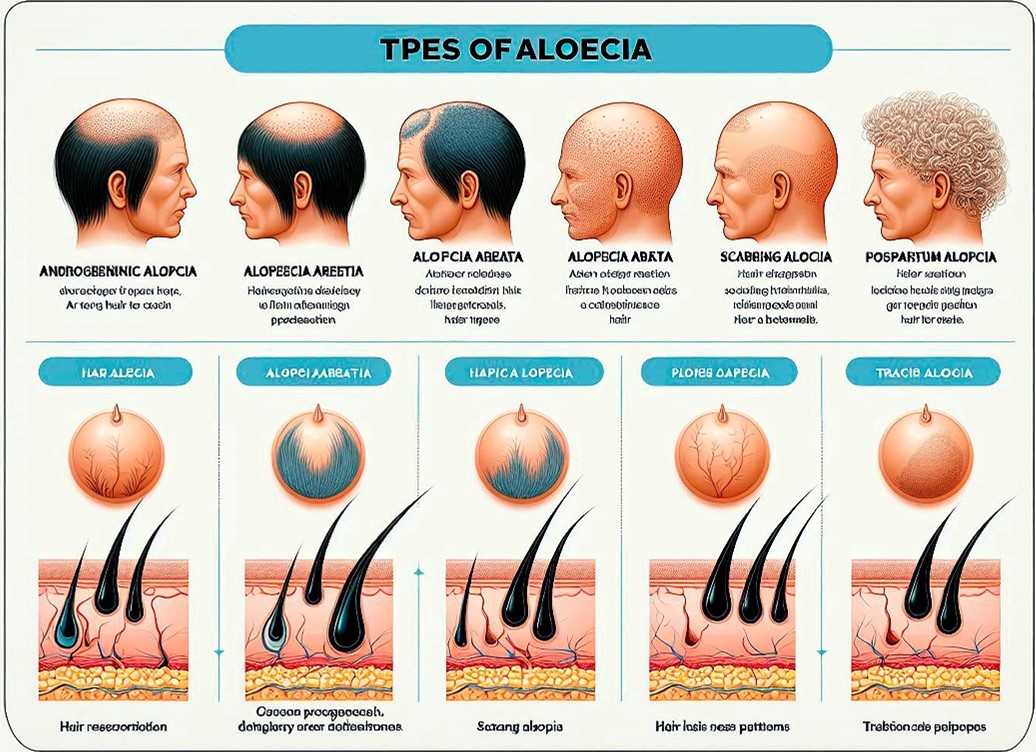

Hair loss is a common concern that affects people of all ages and backgrounds, and as dermatologists, we know that each person’s experience is unique. When it comes to diagnosing and treating hair loss—or alopecia—understanding the different types is essential. Here’s a quick guide to the main types of hair loss, how they present, and what they mean for treatment.
1. Androgenic Alopecia (Pattern Baldness)
Androgenic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss. This type is influenced by both genetics and hormones (specifically androgens) and leads to progressive hair thinning. For men, it often starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown. For women, it usually shows up as diffuse thinning over the top of the scalp. While this type of hair loss is gradual, it’s manageable with treatments like minoxidil or finasteride, and, in some cases, hair transplants.
2. Alopecia Areata (Patchy Hair Loss)
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks its own hair follicles, resulting in patchy hair loss. It can come on suddenly and may affect the scalp or other body areas. The good news? Alopecia areata is often reversible, with hair regrowth possible once the immune response subsides. Treatments typically involve corticosteroid injections or topical medications to calm the immune system.
3. Alopecia Totalis (Complete Scalp Baldness)
Alopecia totalis is a more advanced form of alopecia areata, where hair loss affects the entire scalp. Like alopecia areata, it’s an autoimmune condition. While it can be challenging to treat, some patients respond to immunotherapy or other advanced therapies. Research is ongoing, and dermatologists stay updated on new treatment options as they develop.
4. Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia)
Scarring alopecia, or cicatricial alopecia, is less common but results in permanent hair loss. In this type, inflammation damages and scars over hair follicles, often irreversibly. Causes can range from autoimmune diseases to infections or other skin disorders. Because the hair follicles are replaced by scar tissue, treatment focuses on stopping the progression to prevent further hair loss, typically with anti-inflammatory medications.
5. Postpartum Alopecia (Post-Pregnancy Hair Loss)
Postpartum alopecia is a temporary form of hair loss that some women experience after childbirth due to hormonal fluctuations. The good news? This type of hair loss is usually temporary, with hair often returning to its normal growth cycle within a few months. A dermatologist can recommend gentle hair care tips and supplements to support regrowth.
Remember, if you’re experiencing hair loss, you’re not alone—and options are available.
A visit to a dermatologist can help you understand your hair loss and choose the best path forward.
Your journey to hair health starts with knowledge, support, and the right guidance.
Tags
You May Also Like

Mastering Brevity: Clear & Concise Content Marketing Tips

How to Do SEO for Niche Markets

Understanding AI Overview Fails: Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Previous Post



Leave a Reply